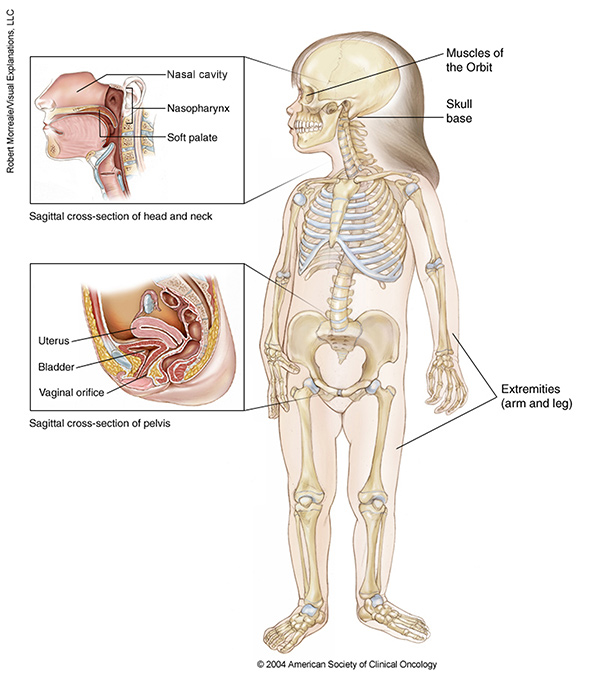
Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma is considered the most treatable form of the disease. The prognosis is also affected by the location of the primary tumour. Orbital and genitourinary track Rhabdomyosarcoma have a better prognosis than do tumours, which originate in the head and neck, extremity, pelvic, and trunk locations.
Prognosis also depends on the stage of the tumour. The Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study Group has defined a set of guidelines, which assign the tumour to groups 1-4 depending on the extent of the disease.
Statistics
- Accounts for 5-8% of childhood cancers.
- 70% of all Rhabdomyosarcoma cases diagnosed in the first ten years of life.
- Usually affects children the ages of 2 to 6 and 15 to 19.
- The peak incidence in 1-5 age group.
- Overall, 50% of the children diagnosed with Rhabdomyosarcoma survive 5 years
Treatment
Rhabdomyosarcoma is treated by a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation.
- Surgery. Resection (removal) of the primary tumour. If necessary after chemotherapy or radiation has shrunk the tumour.
- Chemotherapy. The following chemotherapy agents are commonly used: vincristine, cyclophosphamide, dactinomycin, Adriamycin, ifosfamide, VP-16.
- Radiation. External beam radiation is used in some cases of Rhabdomyosarcoma.